![10 User Research Techniques For UX Designers [Beginner Guide]](https://r2-web.eagle.cool/blog/post/user-research-technique/en/cover.webp)
10 User Research Techniques For UX Designers [Beginner Guide]

Image from Unsplash
If you want to create a user-centered product, service, or user interface, understanding your audience's needs is crucial. This is where user research, or UX research, comes in. As an important part of user experience design, UX research allows you to walk a mile in the user’s shoes and get a clear picture of what your end users think and do and what are the underlying reasons for their actions.
By analyzing your target audience, you will be able to discover weak spots in your product and find the right solution to make it better. Without user research, you might end up with a design that merely looks good but doesn't solve an actual user problem. Interacting with real users before you start the design process will help you avoid guesswork and ground your ideas in reality which in turn will increase your odds of success.
Since time and money are usually limited, understanding the right types of UX research in any project is essential. In this article, we'll guide you through the importance of UX research and introduce some of the key techniques.
What Is UX Research?
User research is a phase in the UX design process aimed at generating insights about your users, their behaviors, goals, motivations, and needs. There are many different techniques that a UX designer can employ to get to know the end user and to identify challenges and opportunities that can improve their user experience.
Usually, UX research begins with designers and researchers examining the real-world needs of the users. This process involves data collection, observation techniques, task analysis, and other feedback methodologies with real participants that aim to get a deeper understanding of what people are looking for when they interact with a product or service.
4 Reasons Why You Should Do UX Research
UX research is the starting point of the UX design process and without it, your work would only be based on assumptions and your own experiences. UX research reduces uncertainty about the user's needs and wants, which can bring many benefits to your product, business, and end users. Here are some of them:
-
Gaining data about the end user.
UX research helps you discover who your end user is, how and when they will use your product, and what problems the product will solve. It can also bring valuable insights to guide your decision between multiple design solutions.
-
Value to business.
By researching the needs of the end user and implementing those design requirements upfront, businesses can make the product development process faster, minimize redesign costs and improve user satisfaction rates.
-
Creating relevant products.
If you don't have a clear understanding of your users, you cannot know if your design will be relevant. Insights brought by user research can ensure your design is relevant to its target audience.
-
Improving the usability of your product.
Exploring user preferences might encourage design tweaks that enable you to design a product that’s a delight to use, delivering a great user experience. It can also give you insights into which features to prioritize.
What Are User Research Techniques: Qualitative vs Quantitative
Most user research techniques can be divided into two types: Qualitative and Quantitative research. You can choose the most appropriate one based on the desired outcome of your UX research.
- Qualitative UX research techniques. These techniques help you answer the question “why?” and find out why something happened based on impressions, interpretations, or prior knowledge of a researcher. Qualitative research is based on an in-depth understanding of human behavior and needs. It’s about recognizing people’s beliefs and practices on their terms.
- Quantitative UX research technique., These techniques answer the questions “how many?” and “how much?”. Quantitative research focuses on numbers, data, and measurable statistics. It can help you quantify the problem and discover patterns that may be useful for deciding what assumptions to test further.
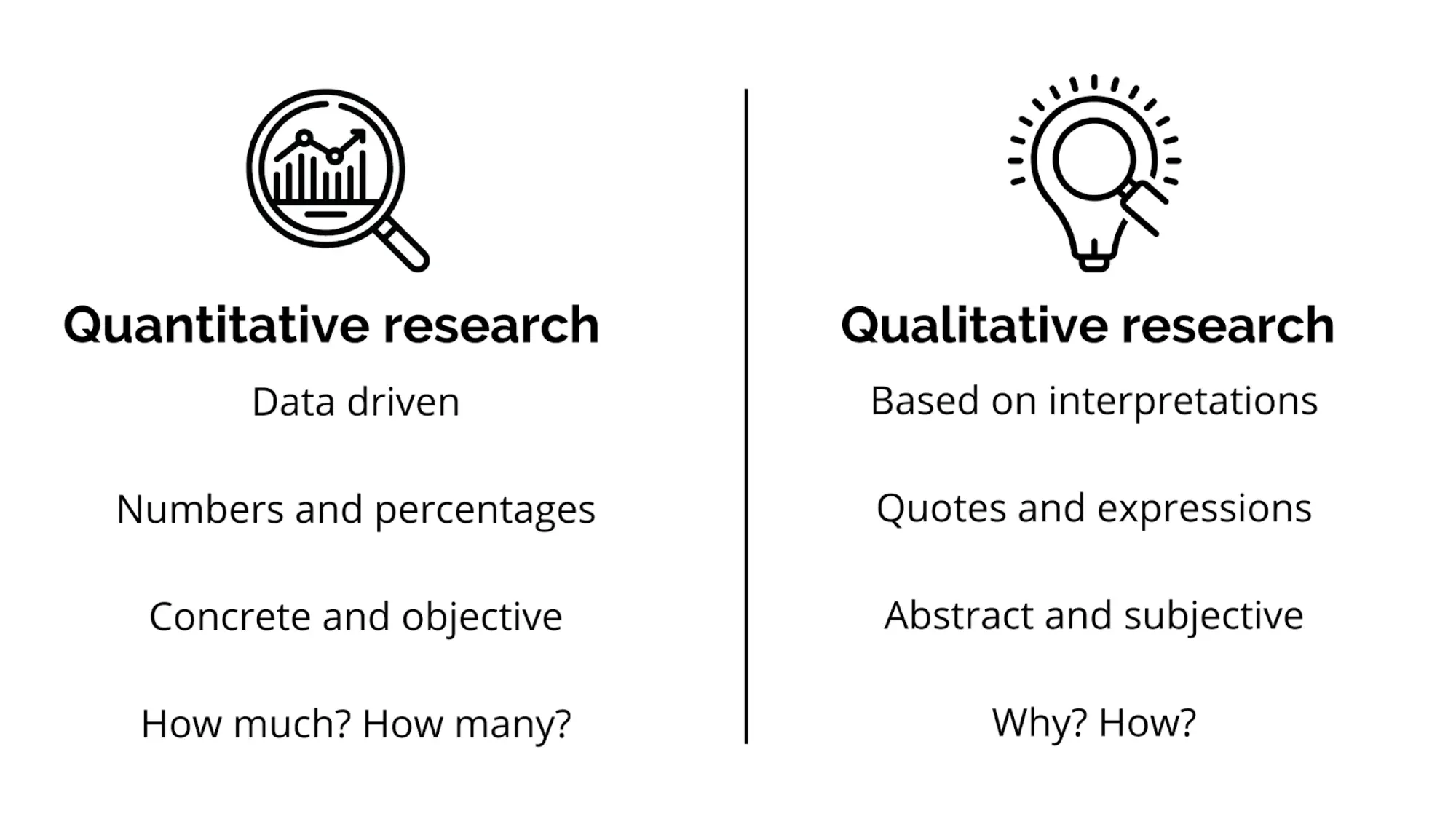
Each of these UX research methods has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it's important to understand your research goals to know which types of research would make the most impact. For example, you can start with qualitative research to get a better understanding of the WHY and use quantitative research to validate these new learnings.
5 Qualitative UX Research Techniques to Improve Your Design
Here are some of the most effective qualitative research methods that will help you explore the behaviors and needs of your users.
1. User Interviews
Image from bickov
An interview is a well-known user experience research method used to uncover the attitudes, beliefs, and experiences of the participants. Typically, an interview is conducted by one interviewer speaking to one user face-to-face, over the phone, or via video streaming.
This method is great for any stage of the project, from planning to testing. During an interview, a UX designer or a researcher asks questions on a specific topic and analyzes the answers. Because of the one-to-one nature of the interview, individual concerns and misunderstandings can be directly addressed and cleared up. Moreover, face-to-face interviews also allow you to capture verbal and nonverbal cues, such as emotions and body language.
When choosing the most appropriate research methodology, remember that interviews can supplement online surveys. For example, carrying out an interview beforehand can help you refine questions for the survey.
2. Focus Groups
A focus group is a research method that involves studying a group of people, their beliefs, and their opinions. Focus group interviews are usually carried out as face-to-face meetings but can also be done via video conferencing tools.
In a typical focus group, a moderator guides five to ten participants through the discussion. Focus groups can be helpful to better understand how users perceive your product, what they see as the most important features, and what problems they experience. One advantage of this method is that users can interact with each other and discuss the topic - this will give you broader insights into what people think about your design.
Here are some tips to help you get the most out of a focus group:
- Have clear goals and ask questions that will get you the responses you need.
- Write a script and note down topics you want to discuss.
- Ask specific questions that are clear and open-ended.
- Invite the right amount of participants.
3. Field Studies
Field studies are all about going out and observing users in their environment rather than your lab or the office. This method is used to measure user behavior in the context where the product will be used which is especially useful if you’re designing an online service that interacts with people's daily lives.
Field study is a great method to reveal context, motivations, or constraints that influence the user experience. Here are the main steps for carrying out this research:
- Recruiting. First, find appropriate people to study. If you have existing customers you can reach out to them. If not, you can try putting out adverts on online platforms, as long as you attract people who match your target audience. 10 - 12 participants should be a decent target.
- Planning. The next thing is clarifying what you will be observing. Is it a very specific task or is it a full process? Define what you’re interested in but don’t structure it too much, your main job is to observe.
- Observation. Next, you’ll need to go out into the field and watch what the participants do. Remember to ask permission to record the events and have a notepad to write down questions or incidents to explore further.
- Reporting. After the observation part, take some time to report on what happened. Include in your report things like person descriptions, quotes, insights, and stories.
4. Usability Tests
Usability testing is the observation of users trying to use your product. It can focus on a single process or a wider range of tasks and can be either moderated or unmoderated. It is the perfect method to use in order to observe directly how people use your app, website, or online tools to get a better understanding if your design is intuitive and easy to use.
If users can’t easily accomplish their tasks during usability testing, there might be some usability problems you should solve. This is why you should make sure to carry out usability testing often, e.g. before you start designing, once you have a prototype, prior to the launch, and regularly after the launch.
Here are some of the reasons that make usability testing a great technique for UX designers:
- It produces specific results and enables you to make decisions based on actual user behavior.
- Clients can participate in the usability testing as observers to clearly who the value of such testing.
- By doing remote usability testing you can save time and money while gaining a wider range of participants.
5. Card Sorting
Image from bickov
Card sorting is a technique that originates from psychological research and is used to discover how users categorize and prioritize information. It can be useful for UX designers if they want to discover how to best structure a website or an app and to find out if your information architecture is heading in the right direction.
In this technique, you write words or phrases on cards and ask users to categorize them. You can also ask them to label the categories. There are three types of card sorting:
- Open card sorting. In this session, users organize topics into categories, generating new ideas and category names.
- Closed card sorting. In this session, you ask users to sort the items into a predefined set of categories.
- Hybrid card sorting. In this case, users are asked to sort cards into categories a researcher has defined, but they also have the option to create new categories.
5 Quantitative UX Research Techniques to Know Your User Better
1. Data Analysis
Using tools like Google Analytics can help you test your assumptions by measuring how people interact with your website or app. You can explore page views, the number of visits, bounce rates, and multiple other metrics.
Monitoring these data can give you valuable information about your users. While quantitative data can give you valuable insights, analytics alone won’t help you identify the “why”, but only “what” and “where”. This is why it’s recommended to use it in combination with qualitative methods like interviews or usability testing.
2. A/B Testing
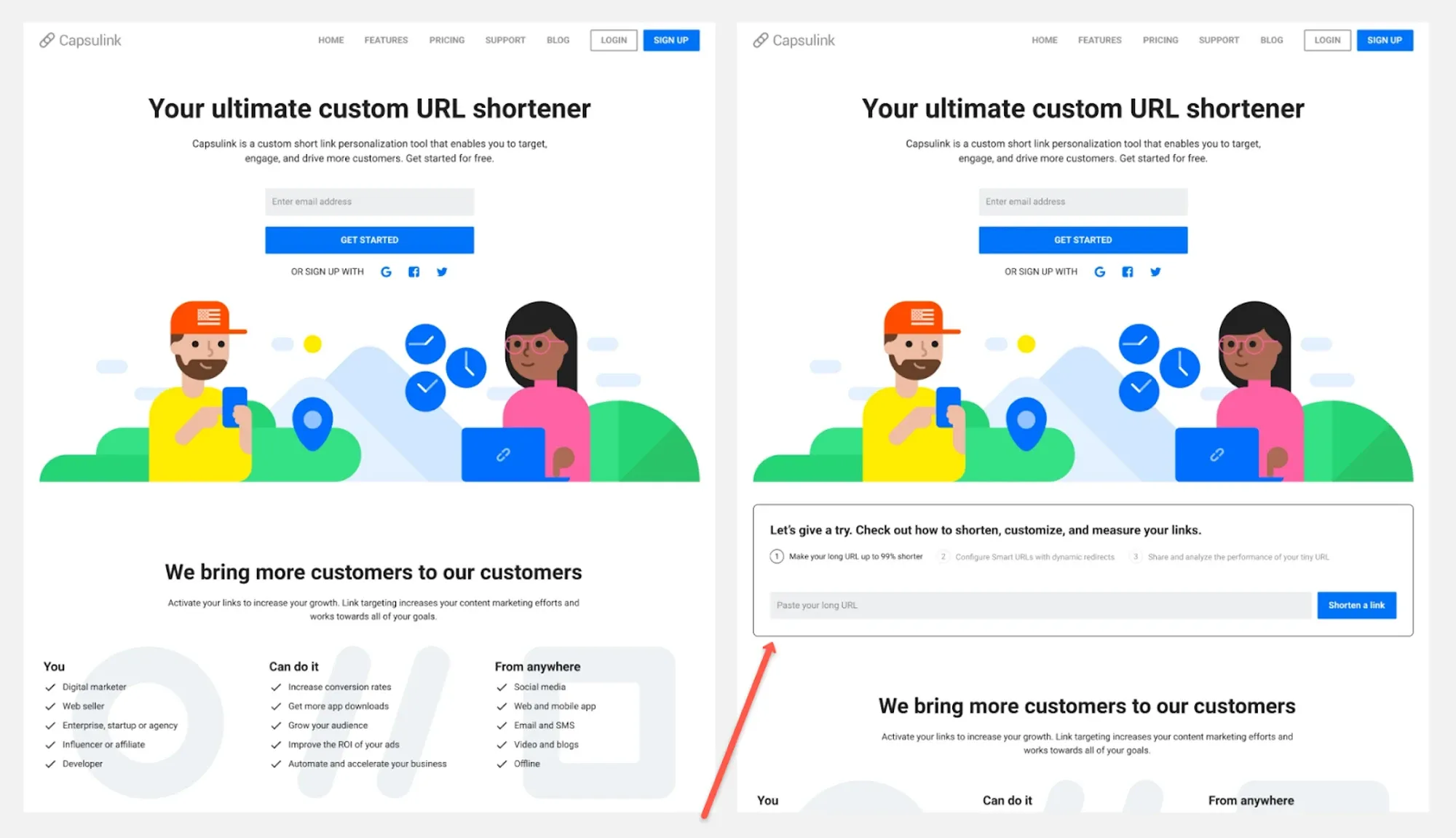
Image from capsulink
If you want to test multiple ideas to see which one works best, A/B testing is the right method to use. With this method, you can test visual preferences, the user experience, or even the text and language.
To carry out A/B testing, you show two slightly different versions of your website or app to an equal amount of users, then review which version performed better. Some variables you can use include button placements, colors, CTA texts, and other elements. This technique is helpful when you want to better understand what works and what doesn’t and what preferences your users have.
When designing a new product, it's crucial to give an opportunity to your potential users to try the product and experience its value as soon as possible. For example, Capsulink A/B tested an element that allowed its users to shorten their links already on the home page which improved conversion rate by 12.8%
3. Eye-tracking
Eye-tracking is the process of measuring where people look and for how long. It allows researchers to evaluate how people search for information on the screen, to find out what parts of your design catch users’ attention and which they skim briefly.
This technique reveals more about your users’ conscious and unconscious behaviors. For UX designers it’s particularly useful as you can uncover things like:
- Gaze patterns - how people scan your content and in what order information is processed.
- Stumbling points - what element caused confusion or takes more time to understand.
- Blindspots – elements that are ignored.
4. Mouse Tracking and Heat maps
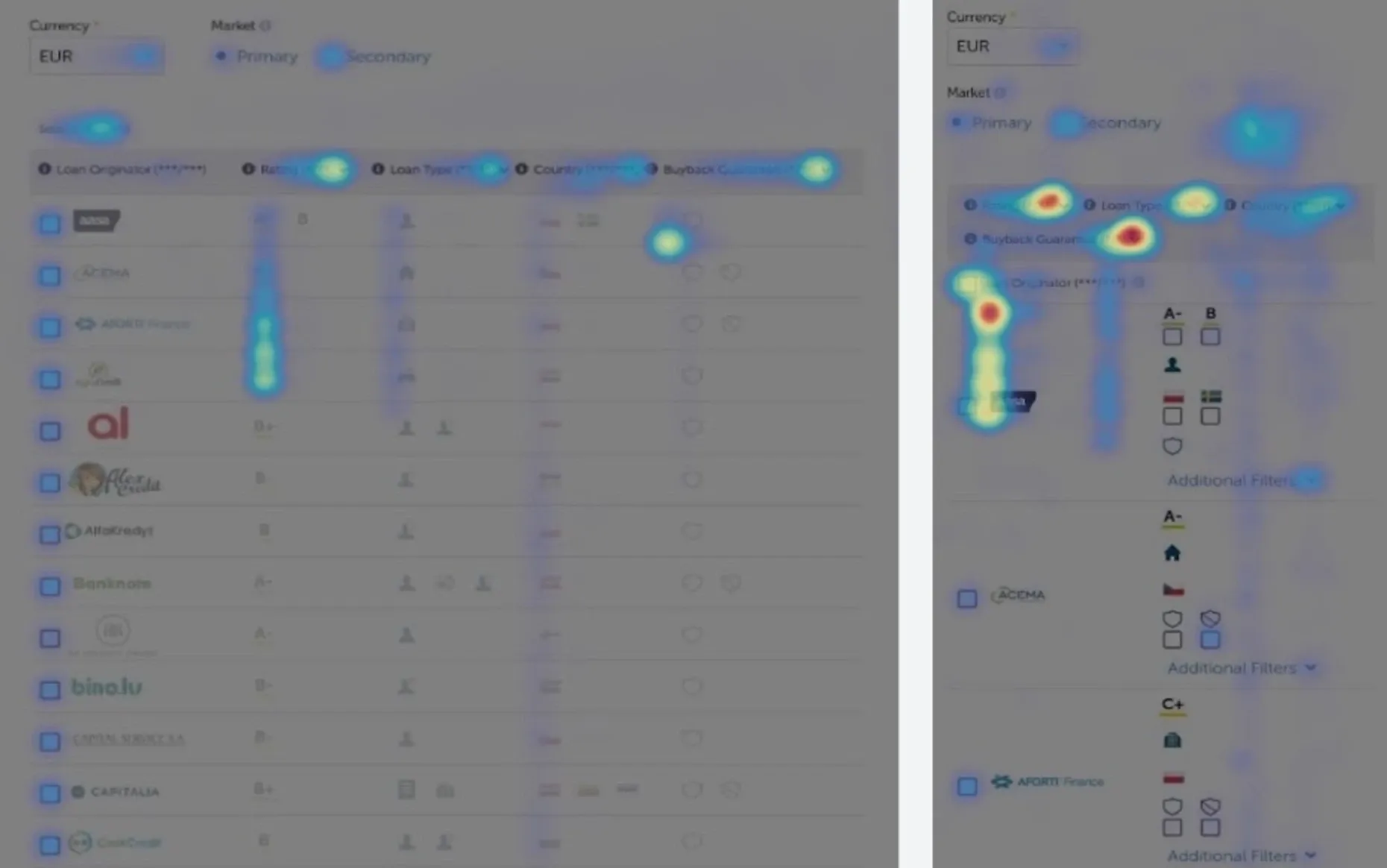
Image from bickov
Mouse tracking involves gathering data from users’ mouse movements on your product. This technique is mainly used to test a prototype or find issues in the ready product. It helps UX designers to preview how the customers use the product, interact with its elements, and how they deal with issues.
With the help of this technique, you can trace how customers navigate your product, where they click, and how deep they scroll. You can also see whether they explore different pages or how long it takes them to find a button and click on it. The advantage of tracking the mouse movements of users is that real user behavior is analyzed, giving accurate information about the user behavior. It also allows UX researchers to process data from a large number of users and identify tendencies.
You can also use heat maps to get a complete view of how users click, scroll, and move on the page. The ‘heat’ part of the name comes from the fact that red illustrates popular (hot) areas of the page, while blue - less popular (cold) areas. Different forms of heat maps include:
- click maps - where users click the mouse,
- scroll maps - where users scroll on the page,
- move maps - where users move the mouse without clicking.
5. Surveys and Questionnaires
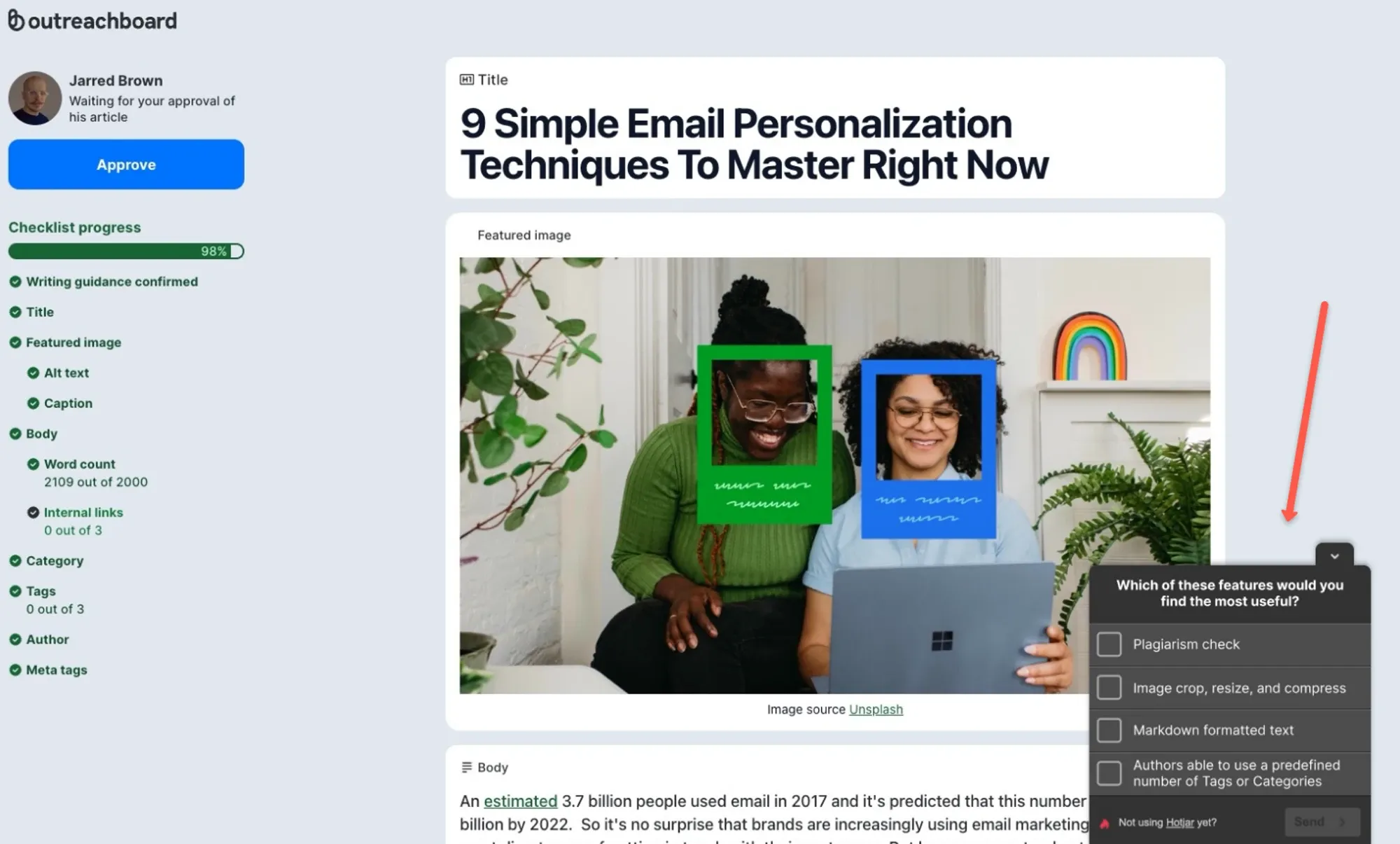
Image from outreachboard
A UX survey collects quantitative and qualitative data about users’ interactions and experiences with the product. Surveys and questionnaires allow researchers to collect user feedback and make sense of user behavior. Based on the survey answers, you can learn what works and what doesn’t, as well as prioritize changes and improve user experience.
When running a survey, it’s important to take the time to plan and formulate your questions correctly. The way you ask a question will determine the responses you get, so keep these things in mind:
- Avoid leading questions. Don’t seek only the data that confirms your beliefs and avoid asking questions in a way that prompts a specific answer from your users.
- Make it quick. Your survey should be brief, especially if participants are not compensated. Only focus on what is truly important, and be as relevant, quick, and as easy to complete as possible.
- Keep it simple. Make sure questions can be easily understood, and avoid complex wording.
- Ask the right questions. Remember to focus your UX survey questions on the problem you’re trying to solve or questions that can help you identify your users' pain points.
Carrying out an on-site survey is a simple but very powerful way to gather valuable feedback from your website visitors. On-site surveys are short and usually slide in from the edge of the page to avoid disrupting a visitor’s journey. For example, Outreachboard asked these questions to its landing page visitors to get a better grasp of their users’ needs and challenges:
- Is anything stopping you from requesting a demo?
- What is your biggest frustration when it comes to guest post editing?
- Which of these features would you find the most useful?
How to Choose the Right Research Technique?
To choose the right research method you have to start by knowing what problem you’re trying to solve and what data you need to gather. Here are a few things to keep in mind when making a choice among research techniques:
- Define the questions you want to answer and work backward to understand the method you should use and the people you need to involve. Consider if you need to talk to people or gather data, is it more important to explore what people say or what they do?
- Think about the stage you’re at in the design process - when you’re just starting out, it’s useful to focus on exploring your users and their problems. Thus, at this early stage methods like field studies or surveys can be helpful.
- When you’ve started to build your product, your UX research should focus on evaluating your designs and whether they address your users’ needs. For this stage choose methods that can help you improve your designs, for example, usability testing or card sorting.
- Remember - even when you’ve developed a working product your research is not done. At this point you want to explore how well the product is performing in the real world, so you should focus on quantitative methods like surveys or A/B testing.
- Consider constraints such as your resources and timeline - some techniques might require specific tools, facilities, and equipment.
UX research is at the core of providing exceptional user experience. Diving deep beneath your assumptions and understanding the needs and goals of your potential users will help you shape your product’s design and create designs that serve customers and businesses more effectively.